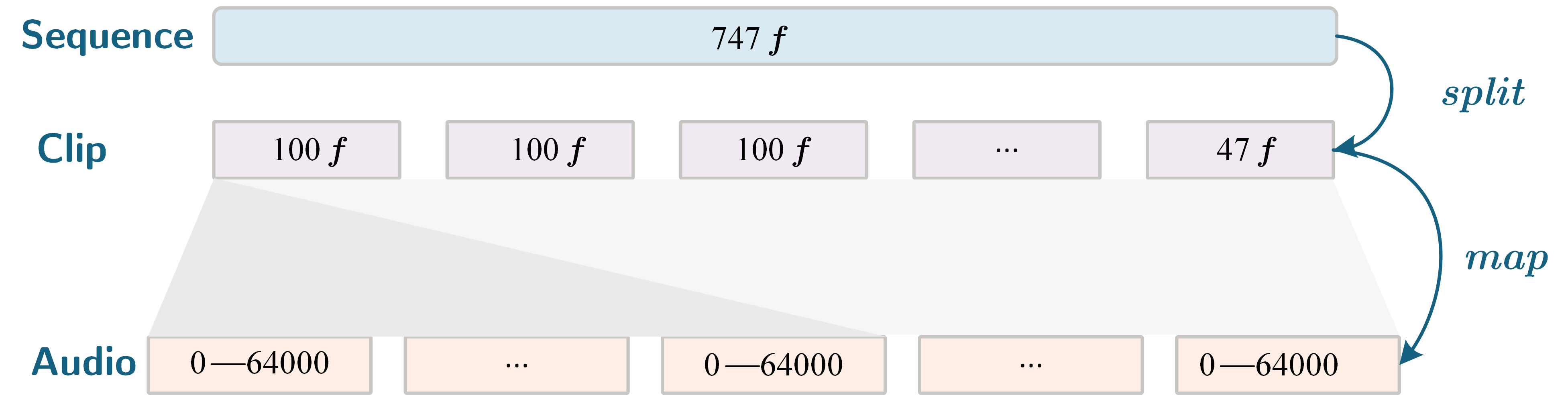
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
| import os
import pickle
import lmdb
import io
import torchaudio
import torch
import numpy as np
from base import Datum, DatasetBase, DATASET_REGISTRY
import logging
logger: logging.Logger
@DATASET_REGISTRY.register()
class HDTF_TFHP(DatasetBase):
def __init__(self, cfg):
root = os.path.abspath(os.path.expanduser(cfg.ROOT))
self.dataset_dir = os.path.join(root, cfg.NAME)
lmdb_path = self.dataset_dir
split_path = [os.path.join(self.dataset_dir, cfg.HDTF_TFHP.TRAIN),
os.path.join(self.dataset_dir, cfg.HDTF_TFHP.VAL),
os.path.join(self.dataset_dir, cfg.HDTF_TFHP.TEST)]
coef_stats_path = os.path.join(self.dataset_dir, cfg.HDTF_TFHP.COEF_STATS)
if coef_stats_path is not None:
coef_stats = dict(np.load(coef_stats_path))
self.coef_stats = {x: torch.tensor(coef_stats[x]) for x in coef_stats}
else:
self.coef_stats = None
logger.warning('Warning: No stats file found. Coef will not be normalized.')
self.audio_unit = cfg.HDTF_TFHP.AUDIO_SR / cfg.HDTF_TFHP.COEF_FPS
self.n_motions = cfg.HDTF_TFHP.MOTIONS
self.n_audio_samples = round(self.audio_unit * self.n_motions)
self.coef_total_len = self.n_motions * 2
self.audio_total_len = round(self.audio_unit * self.coef_total_len)
lmdb_env = lmdb.open(str(self.lmdb_dir), readonly=True, lock=False, readahead=False, meminit=False)
with lmdb_env.begin(write=False) as txn:
self.clip_len = pickle.loads(txn.get('metadata'.encode()))['seg_len']
self.audio_clip_len = round(self.audio_unit * self.clip_len)
subjects_dict = {"train": [], "val": [], "test": []}
for split, fpath in zip(subjects_dict, split_path):
with open(fpath) as f:
for line in f:
subjects_dict[split].append(line.strip())
data_dict = {"train": [], "val": [], "test": []}
for split in ["train", "val", "test"]:
for subject in subjects_dict[split]:
with lmdb_env.begin(write=False) as txn:
meta_key = f'{subject}/metadata'.encode()
metadata = pickle.loads(txn.get(meta_key))
seq_len = metadata['n_frames']
if cfg.HDTF_TFHP.CROP == 'random':
start_frame = np.random.randint(0, seq_len - self.coef_total_len + 1)
elif cfg.HDTF_TFHP.CROP == 'begin':
start_frame = 0
elif cfg.HDTF_TFHP.CROP == 'end':
start_frame = seq_len - self.coef_total_len
else:
raise ValueError(f'Unknown crop strategy: {cfg.HDTF_TFHP.CROP}')
coef_dict = {'shape': [], 'exp': [], 'pose': []}
audio = []
start_clip = start_frame // self.clip_len
end_clip = (start_frame + self.coef_total_len - 1) // self.clip_len + 1
with lmdb_env.begin(write=False) as txn:
for clip_idx in range(start_clip, end_clip):
key = f'{subject}/{clip_idx:03d}'.encode()
start_idx = max(start_frame - clip_idx * self.clip_len, 0)
end_idx = min(start_frame + self.coef_total_len - clip_idx * self.clip_len, self.clip_len)
entry = pickle.loads(txn.get(key))
for coef_key in ['shape', 'exp', 'pose']:
coef_dict[coef_key].append(entry['coef'][coef_key][start_idx:end_idx])
audio_data = entry['audio']
audio_clip, audio_sr = torchaudio.load(io.BytesIO(audio_data))
assert audio_sr == cfg.HDTF_TFHP.AUDIO_SR, f'Invalid sampling rate: {audio_sr}'
audio_clip = audio_clip.squeeze()
audio.append(audio_clip[round(start_idx * self.audio_unit):round(end_idx * self.audio_unit)])
coef_dict = {k: torch.tensor(np.concatenate(coef_dict[k], axis=0)) for k in ['shape', 'exp', 'pose']}
assert coef_dict['exp'].shape[0] == self.coef_total_len, f'Invalid coef length: {coef_dict["exp"].shape[0]}'
audio = torch.cat(audio, dim=0)
assert audio.shape[0] == self.coef_total_len * self.audio_unit, f'Invalid audio length: {audio.shape[0]}'
audio_mean, audio_std = audio.mean(), audio.std()
audio = (audio - audio_mean) / (audio_std + 1e-5)
if self.coef_stats is not None:
coef_dict = {k: (coef_dict[k] - self.coef_stats[f'{k}_mean']) / (self.coef_stats[f'{k}_std'] + 1e-9)
for k in ['shape', 'exp', 'pose']}
data_dict.append(Datum(name=subject, audio=audio, coefficients=coef_dict))
super().__init__(train=data_dict['train'], val=data_dict['val'], test=data_dict['test'])
|